What Are The Communication Between Animals For Gray Fox Whats The Home Range For Gray Fox
There are several red fox subspecies and at least one grey fox subspecies. Let's take a closer look at the red trick vs gray fob to see how they're similar, how they differ, their behavior, habitat, hunting, mating, red trick pups vs gray pull a fast one on pups, and more.
Here's the quick takeaway answer to the red fox vs grayness play a joke on, then we'll get into more detail.
Scarlet foxes have the most colour variation and tend to exist larger than grey foxes. Habitats are similar but gray foxes adopt woods areas. Red foxes accept black legs, a white tail tip, while the gray fox has a black dorsum stripe down its tail. Their diets, behavior, and master predators are also similar.
That's a quick rundown, simply to become into more details, allow's get-go off with the general description of each, then nosotros'll go through other differentiating aspects.
Ruby-red Play tricks vs Greyness play a joke on: General Description
Grey foxes and red foxes share greater similarities with each other than either exercise with their cousin, the arctic fox.
The main characteristic, aside from the colour, is that red and gray foxes are simply more canine in nature than the chill fox.
Y'all tin observe out more about the chill fox hither. Which are often thought to be the smartest play a trick on breed.
Gray foxes are adapted to climbing trees and can climb trees vertically. But in comparison, they're not quite equally fast on their anxiety, or every bit agile as cherry foxes.
The carmine fox, while having very similar physical features, is larger, and is the more well-known and widespread of the two species.
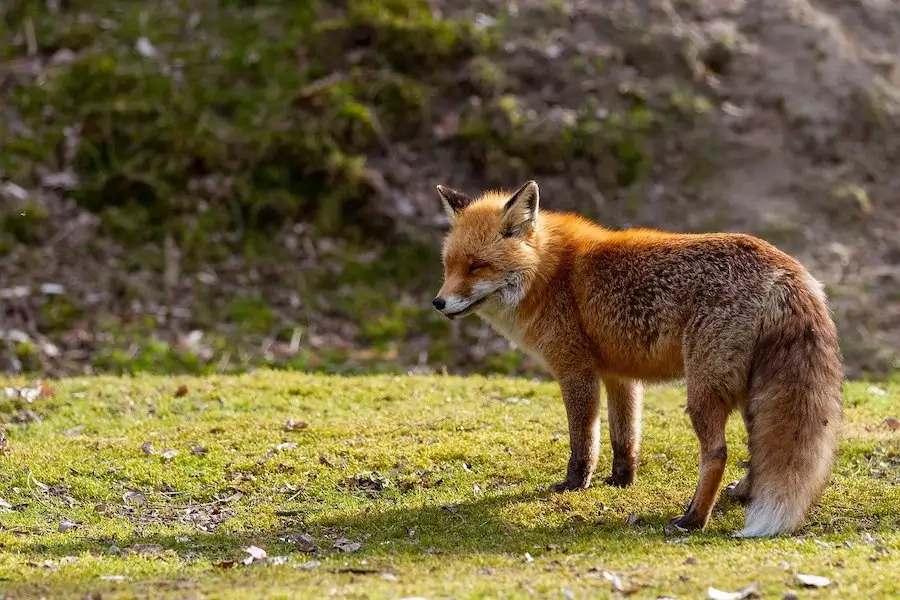

Fox coloring
Cerise foxes Named after their ruddy fur which tin can range from bright orange to dark brown, but the color pallet is actually wider than this.
In fact, scarlet foxes have over 100 color variations across the species.
This can even extend through to a more silver color, which can make full identification difficult. Simply there are other features that usually set them apart…
For the majority of the fourth dimension, the ruby foxes' red coats tend to exist a dark brick-red color, with the exception of their blackness legs, ears, and tail tip which is white.
Their white-tipped tails are blackness at the base of operations, which makes it easier to distinguish them – fifty-fifty when they're running.
The red coat becomes gray at the muzzle while their belly fur is almost foam-colored.
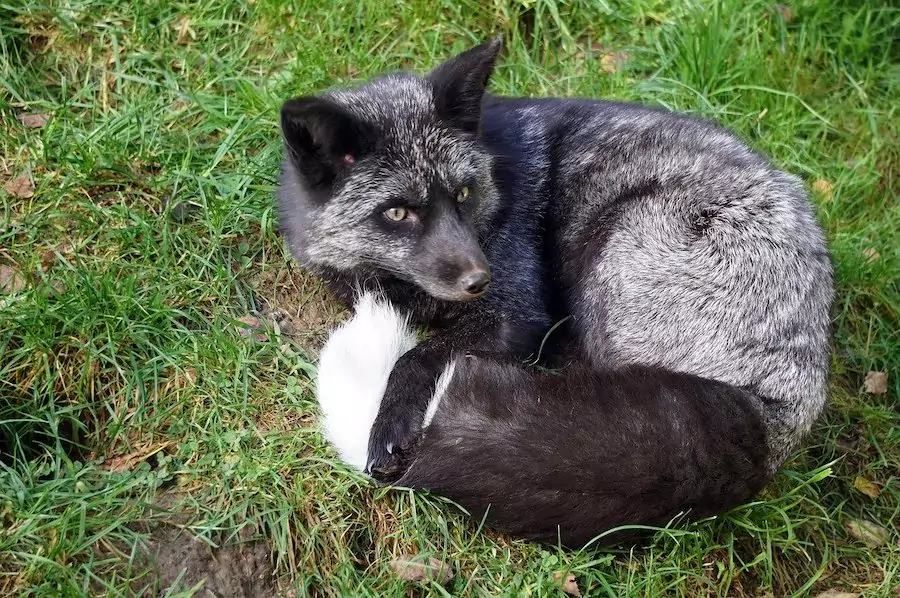
By contrast, gray foxes are ever a standard short-haired gray color, they do not have color variations.
The gray fox's tail has shorter pilus that is grayness on the underside and a singled-out black stripe running downward the back.
Gray foxes have a pale underside with dark, short fur on their back, which oftentimes makes it look two-toned. Not as well dissimilar to a wolf or a coyote who are as well part of the Canid family.
If a fox is running, you might likewise see that if the tail is held up while running and so it'due south most probable a grey fox.
You might also then encounter the unique black stripe down their tail which all gray foxes will have.

Red fox vs Grayness fox: Size and Weight
In terms of height and weight, red foxes are slightly taller and heavier than gray foxes.
Gray foxes have a smaller overall build than red foxes, with adults weighing between four and eight pounds. Ruddy foxes typically abound to virtually 20-30 pounds in weight, slightly more than gray foxes.
For both species, the males are typically larger than the females. Just at that place are sometimes exceptions.
| Ruby Play a trick on | Gray Fox | |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Summit | xviii – 24 inches | 12 – xvi inches |
| Avg. Weight/Mass | 30 lbs | viii.five lbs |
Blood-red vs Grey fob: Concrete Characteristics
Both ruby-red and gray foxes take the aforementioned number of teeth (42), but red foxes have longer canine teeth. This helps them rip through their casualty.
The ears of a gray are much bigger than those of a crimson, which is an adaptation that allows them to hear their prey in the brush. Their tails as well help with balance while they're running after casualty or climbing trees.
Carmine fox vs Grayness play a joke on: Lifespan
Red foxes live for around 4-five years in the wild or 14 years in captivity. While grayness foxes can alive up to 6 years in the wild and fifteen years in captivity!
Hither's an extract from the full table below showing their lifespan and likewise compares that with the arctic fox. For more data see the larger summary table further below.
| Red Fox | Grey Fox | |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan in the Wild | 3-four years | five-six years |
| Lifespan in Captivity | fourteen years | 15 years |
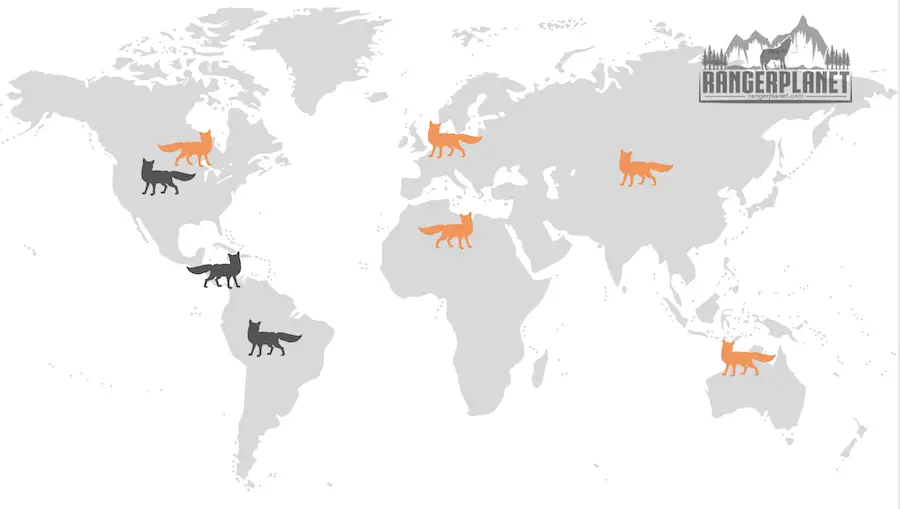
Red fox vs Grey fox: Geographical Location
Both cherry foxes and gray foxes live throughout the Northern Hemisphere with cerise foxes being more predominant in Europe, North America, and Asia. And gray foxes in North America, Key, and Southward America.
Red foxes also inhabit Africa but do not by and large live in the Southern Hemisphere
| Red Flim-flam | Gray Fox | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Europe, N America, and Asia | North America, Central, and S America |
Scarlet fox vs Greyness trick: Habitat
The two species besides tend to reside in dissimilar habitats merely Both red and gray foxes live throughout Northward America and Eurasia. Red foxes do not generally live in tropical or subtropical climates.
The red play tricks prefers open up fields and grasslands, with woods nearby for hunting prey. They as well similar areas with low and varied vegetation where they can hide from danger.
Grayness foxes prefer to live in hardwood forests or a mix of hardwood and softwood forests that provide dense foliage.
Carmine fox vs Gray play a trick on: Territory
Nearly fox territories are nigh 2 or 3 square miles under platonic habitat circumstances, although if the hunting proves prosperous, most foxes will stay inside a square mile each day.
How foxes mark their territory
A fob will mark its territory by digging small-scale holes around its boundaries, leaving behind a secretion from glands that are both from perspiration, and sebaceous scents.
All these marks together are known as a 'scent drag'. Their urine is as well used to leave other markings inside their territory – they dig pocket-sized holes in which they urinate.
Scarlet fox vs Grayness fob: Advice and Interaction
1 way cherry foxes communicate is by leaving odor markings in their territory via glands. They accept aroma glands on the throat, at the corner of their eyes, between their toes, and on their tail.
Gray foxes are similar, they too mark their territory with urine by spraying information technology onto rocks or copse. Males do this more frequently than females.
When a grayness play a joke on is frightened or feels threatened, it makes a loftier-pitched bark or yap to signal danger.
Gray Foxes make barking sounds likewise when communicating with each other, especially earlier eating or after seeing danger.
These barks are brusque but loud. They are also known to bark in a "wow-wow" sound.
When a gray play a joke on is frightened or feels threatened, information technology makes a high-pitched bark or yap to point danger.
Foxes oftentimes communicate with one another through postures, expressions, and movements.
A fox shows submission to some other dominant pull a fast one on past standing still and holding its tail downwards. Information technology may even curlicue over and present its vulnerable belly.
A red play a trick on flattens its ears and holds its tail downwards or between its legs. It may yelp, whine, howl, bark, growl, wail, or scream if information technology feels threatened. A carmine fob as well snarls at other animals to warn them to stay abroad.
Red foxes make barking noises when they are excited …or show aggression toward other crimson foxes.
Red fox vs Gray fox: Hunting and Diet
Both red foxes and gray foxes can vary slightly in their dietary habits …depending on what food source is bachelor at the fourth dimension.
Because of these variations, grays are more likely to be omnivores while the reds tend to be more cannibal in their option of diets.
To impale their casualty, both flim-flam species use short bursts of speed to surprise their casualty before the casualty tin can react. Or dig to discover and suspension into burrows to access casualty.
Cherry-red foxes tend to prey on large mammals such as rabbits, squirrels, birds, mice, and poultry. Or smaller animals such as rodents that reside in their burrows.
They also eat insects when other food is scarce but not usually at the levels necessary for them to be a major part of their diet.
Red foxes have even been known to take hold of freshwater fish and even frogs!
Gray foxes don't unremarkably catch animals as large as those caught by carmine foxes, all the same, they have been known to go later calves, and small livestock such as pigs, merely mainly feed on small rodents such as mice.
Alongside this, gray foxes will eat fruits, vegetables, and berries whereas reds will consume rodents and lots of other types of food.
Both carmine and gray foxes will also feed on carrion, and they volition consume eggs if the opportunity arises.
Explore their diet farther with our article on what foxes eat. And also find out more about what arctic foxes eat.
Cerise play a joke on vs Gray play tricks: Predators
Both the red play a joke on and the grayness play tricks are the target of a number of predators.
The most mutual include birds of prey, such as eagles and hawks, large cats, wolves, coyotes, bears, and cougars. These predators usually snatch red foxes out of their dens or kill them by ambushing.
You can notice out more about what eats foxes here.
Red foxes, with a greater chapters for speed than gray foxes, will endeavor to outrun predators if and when they can.
The gray fox will make every endeavor to escape from predators by running up a tree or towards a body of h2o. See, tin foxes swim.
Red trick vs Grayness fox: Behavior
Adult male ruddy foxes volition marker their territory past urinating on trees, logs, or rocks. Greyness foxes do not have the same need since they are solitary animals that just come up together for the breeding season.
Gray fob beliefs is typically not-aggressive against humans. Carmine play a joke on behavior tin be more aggressive depending on the activity of humans in their environment.
Red fox vs Gray play a joke on: Social and Mating Habits
Generally speaking, red foxes tin can be lonely but often live in dens that tin can comprise multiple family unit members including pups.
Gray foxes are alone animals except for the breeding season. Red foxes breed all year circular, but February to March is their height mating season.
The gray pull a fast one on gestation period is typically 52 days. They give birth to a litter of 3 or iv kits, which are built-in blind and without fur.
Red foxes will come together to breed generally effectually February to March, just it is not uncommon for them to breed year-circular.
During mating season, cerise foxes will form a family-based group consisting of one male and several females. The female has a gestation flow of 51-53 days, and as with greyness foxes, the immature are born bullheaded and without fur.
Blood-red flim-flam pups vs Grayness play tricks pups: Rearing and Development
Although both species accept pups, gray foxes have them in late winter or early spring, which is during the mating flavour of greyness foxes. Red foxes can requite birth at any time throughout the yr depending on where they live.
The reason why grayness fox pups are built-in at this time of year is that it gives them some advantages over some principal predators as there is more food around for them while other predators may have migrated or are hibernating.
In early jump, around a month after being born, kits of both carmine and gray fox species volition open their eyes and begin to explore outside the den with their female parent in tow. At this point, they volition brainstorm to eat solid food and eventually hunt on their own.
Gray fox pups are not very vocal …but they exercise make high-pitched sounds – these tend to be used when mother and pups are separated.

The easiest way to tell a blood-red fox from a gray fox
Overall, the chances are it's a gray fob, every bit that is the most common species to see in and around urban areas. This is confirmed further if it is a shade of red, and if the tail is slightly bushier.
But if making the stardom is nonetheless hard. Then look for a blackness downward the upper side of the tail, this would hateful it's a grayness fox. Especially if the tail is raised when they're running. Merely when the tail is hanging down, it's a red play tricks.
If you are in North America, then look for this other fundamental distinction – the gray fox has a white-tipped tail, whereas the scarlet flim-flam's tail is entirely black at its tip.
Simply if they move around every bit a pair or as a small group. So there is nothing to worry about every bit those volition be immature pups from those two species of foxes. A group may as well mean it's an arctic pull a fast one on if y'all're in a cold or tundra region.
As a quick reference guide, here'south the table which outlines the differences between reddish fob, grayness pull a fast one on and also includes the arctic fox for comparison.
Blood-red trick vs Gray fox: Comparison Table
| Cherry-red Fox | Gray Fox | Chill Play a joke on | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Vulpus vulpus | Urocyon cinereoargenteus | Vulpes lagopus |
| Color | Mostly blood-red. Just up to 100 Color Variations | Gray only | Gray or wintertime white |
| Agile Hours | Crepuscular | Nocturnal | Crepuscular |
| Lifespan Wild | iv-5 years | v-6 years | iii-4 years |
| Lifespan Captivity | xiv years | 15 years | fourteen years |
| Height | 18 – 24 inches | 12 – 16 inches | 10 – 12 inches |
| Avg. Weight/Mass | twenty lbs | 10 lbs | 10 lbs |
| Location | Europe, North America, Asia, Commonwealth of australia, and North Africa | N America, Central, and South America | Chill Tundra and around chill fringes |
| Habitat | Mixed mural, and mixed climates | Dense hardwood or hard/softwood forests | Chill tundra, chill fringes |
| Distinctive Markings | Redish back, black legs, and a bushy tail | A blackness line forth the meridian of the tail | White, Shorter ears, and muzzle, thick fur |
| Group | Solitary or Pairs | Solitary | Lonely or small-scale groups |
| Breeding Season | February – March, only tin be all year round | February – March | March – April |
More fox assist
We promise this has helped you to understand the differences and similarities between carmine foxes and greyness foxes. We have more fox resources here on Ranger Planet. Bank check out some of the related manufactures below…
Facts about fennec foxes
What do chill foxes eat
Practise arctic foxes hide
Can foxes swim

Source: https://rangerplanet.com/red-fox-vs-gray-fox-differences-how-to-identify/
Posted by: mcleanyoureput.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are The Communication Between Animals For Gray Fox Whats The Home Range For Gray Fox"
Post a Comment